 Diversity of heatsources
Diversity of heatsources
 Japanese
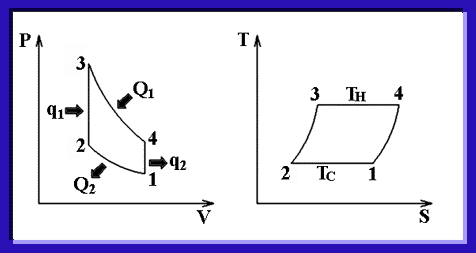
JapaneseOn thermodynamics, it can explain that Stirling engine is an regeneratable external combustion engine using Stirling cycle. Stirling cycle is composed by constant volume heating process, isothermal expansion process, constant volume cooling process, and isothermal compression process. For heat efficiency of this cycle, by using heat, which is discharged to the engine outside by constant volume cooling, for a constant volume heating, as being equal to a thermal efficiency of Carnot cycle that have theoretically highest thermal efficiency. Also, this means Stirling cycle is a reversible cycle. Then it is able to make engines, which driven with an outside power, work as a refrigeration machine.
A general Stirling engine makes gas go and return between two space attached temperature differences and make a pressure variation occur. These two space are ideally sealed up, and then there isn't gas exchange with the outside. As being able to work anywhere, if there is a temperature difference, Stirling engine is expected various applications in future.
 Diversity of heatsources
Diversity of heatsources
 Clean exhaust gas
Clean exhaust gas
 Superb quietness
Superb quietness
 High theoretical thermal efficiency
High theoretical thermal efficiency1-Tc/Th
Where
Th : Higher temperature in the cycle
Tc : Lower temperature in the cycle
This means as to be large for a temperature difference, theoretical heat efficiency are higher. Among Stirling engine developed, the engine to achieve a thermal efficiency 40 % exists.
 Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
 Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition
Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition