
Working principle of the Stirling engine
 Japanese
Japanese
Ideal working principle of Stirling engine
This figure shows the ideal working principle of Stirling engine. Gas expands, as it warms and compresses, as it cools. Stirling engines move by using this characteristic of gas. However��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������nstant volume. The gas pressure inside an engine increases.
2-3 : Isothermal expansion process
The gas expands as keeping a constant temperature. The engine works to the outside.
3-4 : Constant volume cooling process
The working gas is cooled with constant volume. The gas pressure inside the engine decreeses.
4-1 : Isothermal compression process
Gas commpresses as keeping a constant temperature. The engine discharges the heat to the outside.
Working principle of the Displacer type Stirling engine
A displacer type Stirling engine makes working gas go and return between high temperature space and low temperature space by a displacer piston, and output the pressure variation that occurs by this gas movement as power by a power piston.
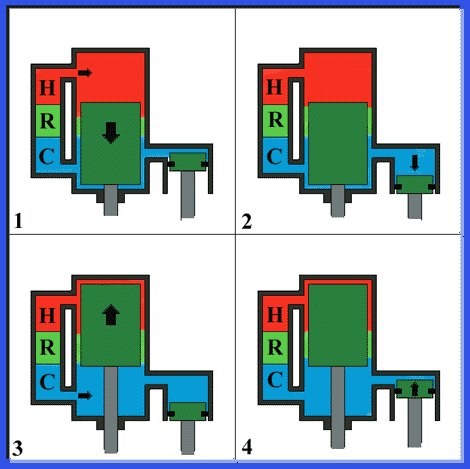
Working principle of the Displacer type Stirling engine
- 1 : Constant volume heating process
- By the displacer piston moving to the side of compression space, the working gas in the engine becomes a higher temperature and flows to the expansion space, as passing through the heater. The gas pressure in the engine increases.
- 2 : Isothermal expansion process
- By the pressure increased in engine, the power piston is pushed. The engine works to the outside.
- 3 : Constant volume cooling process
- By the displacer piston moving to the side of expansion space, the working gas in the engine becomes a lower temperature and flows to compression space, as passing through a cooler. The gas pressure in the engine drops.
- 4 : Isothermal compression process
- The power piston is pushed, and the engine is worked from the outside and discharges heat to the outside.
With an actual engine, both pistons don't move intermittently but sinusoidaly. By attaching a phase angle of 90 degree between a movement of both pistons, engines get a cycle that has such like these processes.
Working principle of the 2-piston type Stirling engine
With 2 piston type Stirling engine, a movement of the working gas and output of power is done by two power pistons. A phase difference of 90 deg. is attached to both power piston displacement.
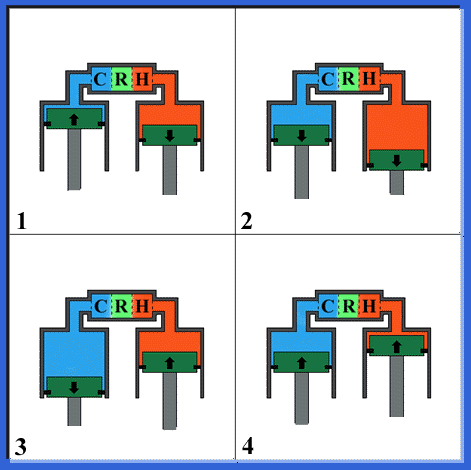
Working principle of the 2-piston type Stirling engine
- 1 : Constant volume heating process
- With this process, the power piston on the side of a compression is upper, of expansion moves under. Working gas in the engine becomes a high temperature and flows to expansion space, as passing through a heater. A gas pressure in the engine increases.
- 2 : Isothermal expansion process
- In this process, both power pistons move to the lower side, and the working gas expands. The engine works to the outside.
- 3 : Constant volume cooling process
- In this process, the power piston on the side of a compression is lower, and of expansion moves upward. Working gas in the engine becomes a low temperature and flows to the compression space, as passing through a cooler. The gas pressure in the engine drops.
- 4 : Isothermal compression process
- In this process, both power pistons move upward, and the working gas is compressed. The engine is worked from the outside and discharges heat to the outside.
With an actual engine, both pistons can not move intermittently. By attaching a phase angle of 90 deg. between both pistons that move sinusoidaly, engines have above-mentioned processes approximately.
 Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
 Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition
Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition


 Japanese
Japanese



 Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University
Return to Stirling Engines of Saitama University Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition
Return to Stirling Engiene Home Page Academic Edition