System Engineering & Safety Technology Research Group
System Engineering & Safety Technology
Marine transportation of radioactive materials plays a crucial role in the nuclear fuel cycle in Japan. Recently, the cargo has been diverse, and the transportation volume has been increasing. Under this situation, demand for ensuring the safety and security of transport is growing.
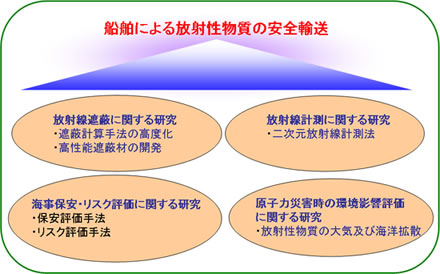
This group conducts research on the following subjects to ensure the safety and security in maritime transport of radioactive materials:
- Assessment technology of radiation shielding.
- Radiation measurement technology.
- Risk assessment/safety assessment technology.
- Environmental impact assessment technology, etc.
This group contributes to maritime administration by conducting safety assessments for nuclear fuel material transport containers and vessels and by providing technical support and new technologies related to rule revisions and international safety standards.
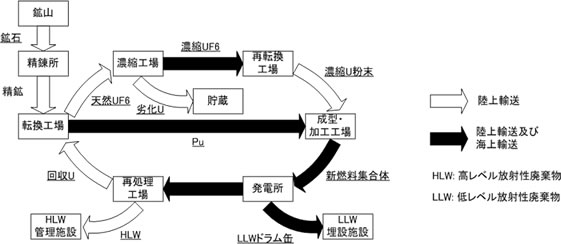
Conceptual diagram of nuclear fuel cycle and transportation in Japan
Conceptual diagram of nuclear fuel cycle and transportation in Japan
Recently, this group has been focusing on research on risk-based safety assessment methods aiming to reflect the knowledge gained from these studies on not only the risk assessment of radioactive material carriers but also the risk assessment of ships in general.
Members
(◎: Head of the Group)
- Mitsufumi ASAMI(Concurrent post)
- Junichi KUDO(Concurrent post)
Main Research Topics
Survey of radioactive material concentration distribution in sea area and estimation method of radioactive material concentration in seabed soil
Due to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident following the Great East Japan Earthquake, radioactive materials were released into the atmosphere and ocean. To understand its impact on fisheries, to protect the environment of the sea area, and to understand the environmental dynamics, it is necessary to know the situation of radioactive substances distribution in the sea area for medium- to long-term. NMRI collaborates with the University of Tokyo on the surface mapping of the radioactivity concentration in the seafloor through the Nuclear Regulatory Agency project, etc., and also studies the method for estimating the temporal change in the radioactivity concentration in the seafloor by ocean diffusion simulation.
We are also conducting the following research:
- Study on improvement of shielding safety evaluation method using the Monte Carlo method for a radioactive material transportation container.
- Study on environmental impact assessment system for accidents during the radioactive substances transport by ships.
- Study on risk assessment method for radioactive transport.
- Development of risk-based design support tools (fire, evacuation, and chemical substance diffusion simulation).
Research Facilities
Shielding laboratory
In the shielding laboratory, we conduct experiments to evaluate the shielding performance of resins, serpentine concrete, boric acid water, etc., used as high-performance neutron shielding materials. In addition, we assess the shielding performance of models of spent fuel storage containers (casks) for transportation. Furthermore, we conducted experiments to develop new shielding material with Akita University using a neutron source (Calfornium-252) and a gamma ray source (Cobalt-60).
These experimental results include secondary gamma rays generated from thermal neutrons in addition to neutrons and primary gamma rays. With these data, we conduct detailed analysis using the continuous energy Monte Carlo code MCNP (Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code) to improve and standardize the shielding performance evaluation method.

Transport container model
