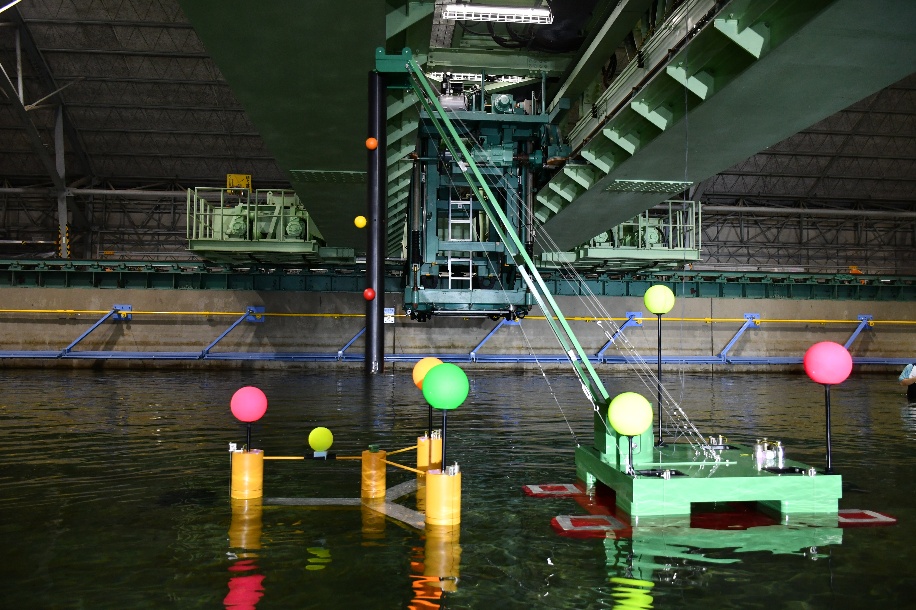
Overview of Ocean Engineering Basin
Research Overview
Facilities Overview
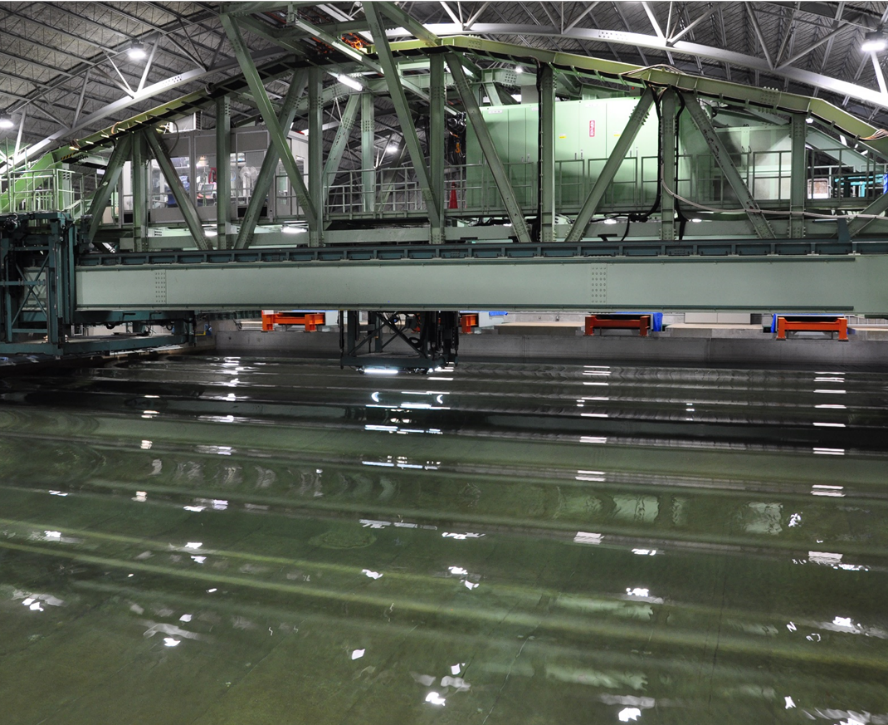
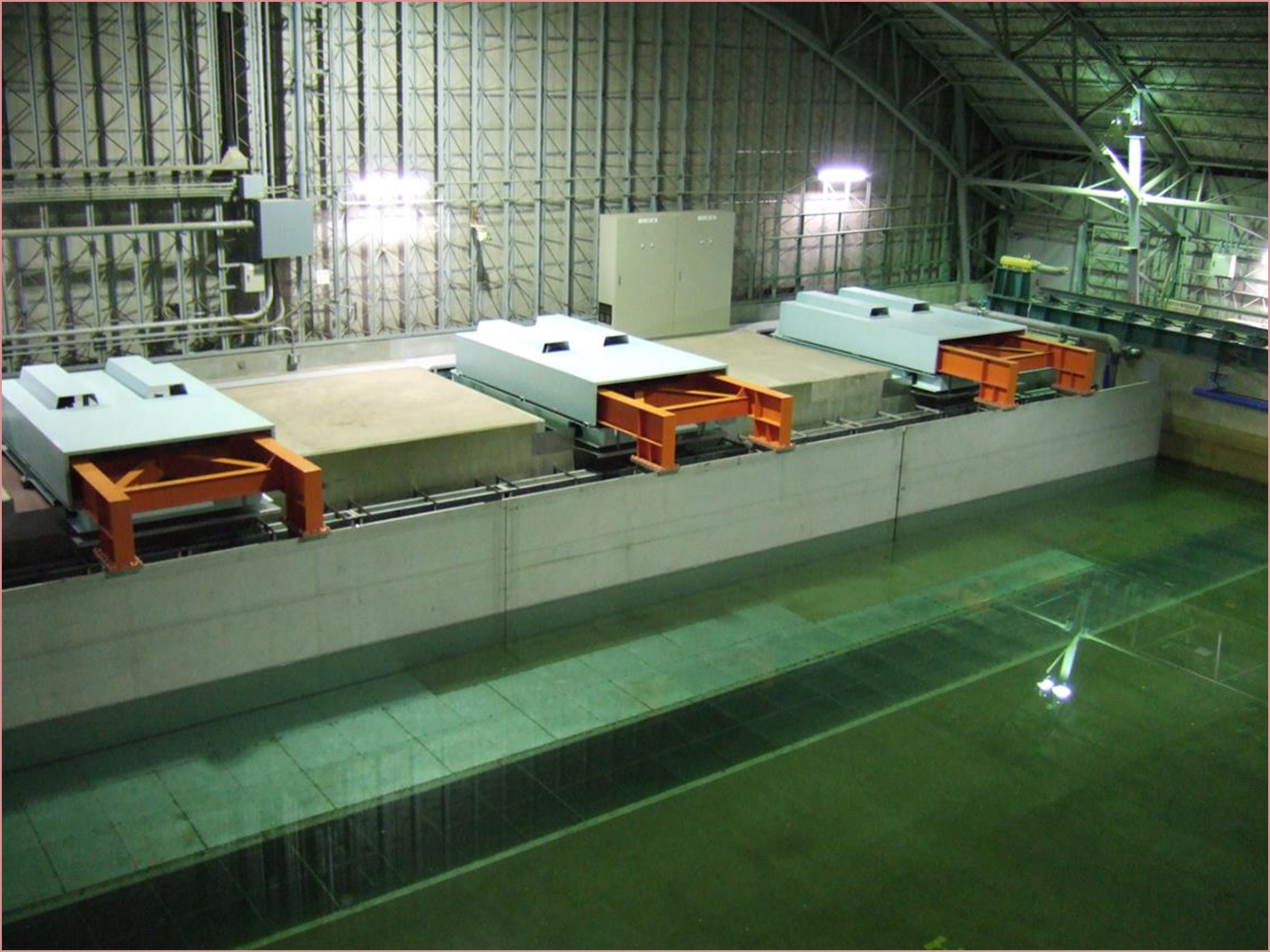
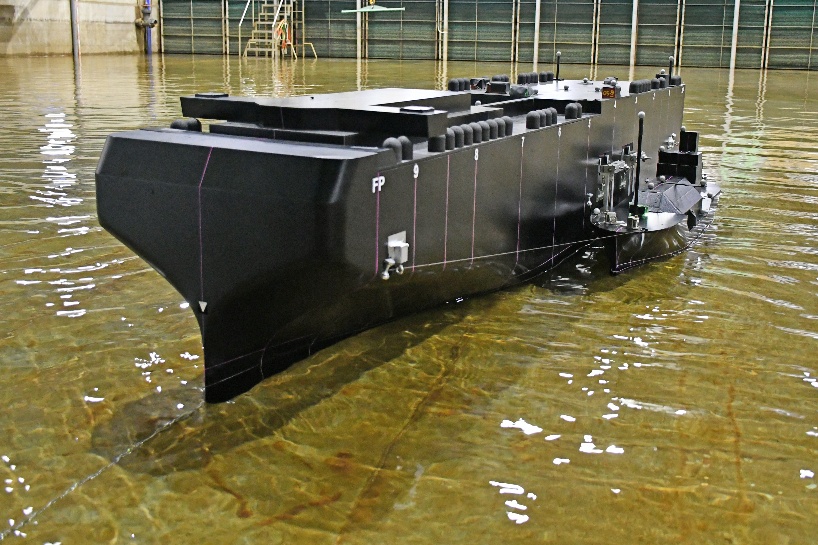
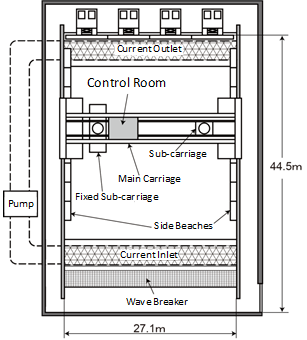
The Ocean Engineering Basin was built in March 1978 as a research facility to promote research and technological development related to marine development. Since its construction, NMRI has renovated the Ocean Engineering Basin to meet changing societal needs and research subjects. It is the only experimental basin in Japan with the features of a large square tank capable of testing under the combined external forces of wind, waves, and currents, as well as variable water depth, allowing model tests in shallow water. The basin is equipped to carry out various tests, including towing tests to measure hydrodynamic forces on various floating structures, including ships; motion measurement tests under combined environmental forces (wind, waves, currents) for moored floating structures; and position-keeping performance evaluation tests for Dynamic Positioning Systems (DPS).
Research Facilities and Main Equipment
【Towing carriage】
It is an XY (2-axis) type towing carriage, and the traveling main carriage can travel at a maximum speed of 0.7 m/s and the traveling sub-trolley at a maximum speed of 0.5 m/s. It is equipped with a fixed sub-carriage that can move to any position, and both the traveling sub-trolley and the fixed sub-carriage have turntable functions (Ψ-axis rotation) and lifting functions.
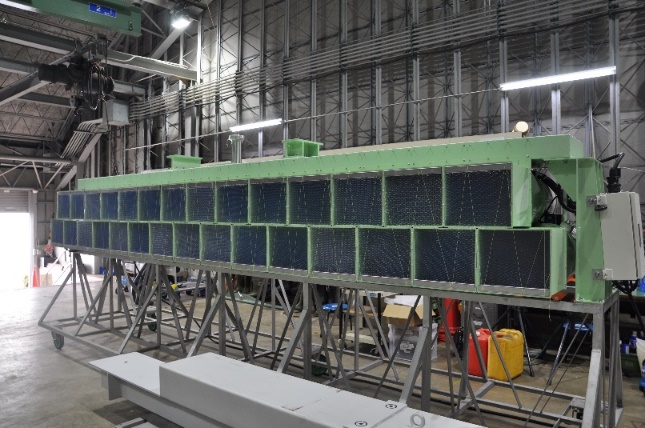
【Wave generator】
It is a piston-type wave generator and can create regular waves, irregular waves (JONSWAP, ISSC, ITTC, Ochi-Hubble, Bretschneider-Mitsuyasu), and arbitrary waves (arbitrary time series, arbitrary spectrum). The wave periods that can be generated range from 0.7 to 3.0 seconds, with a maximum wave height of 0.6 meters.
【Current generator】
It is a recirculating current generator using an impeller capable of generating a uniform flow near the center of the tank. The maximum flow velocity that can be generated is 0.3 m/s.
【Wind generator】
It is a multi-stage wind generator, capable of generating wind speeds of up to 12 m/s for the horizontal arrangement type and 10 m/s for the rectangular arrangement type.
Examples of actual basin use and testing in recent years
【Priority Research】
- Research on comprehensive safety assessment technology for offshore natural gas production systems, etc. (FY2011-2015)
- Research on the development of project certification support technology for marine resource development (FY2016-2022)
- Research on the development of comprehensive safety assessment technology for offshore resource development systems (FY2016-2022)
- Research on equipment and operational technologies for ocean development (FY2023-2029)
【Fundamental Research】
- Study on estimation method of dynamic mooring tension acting on mooring lines (FY2018-2019)
- Model-based control system design for submarine equipment installation work vessels (FY2018-2020)
【JSPS Grant-in-Aid】
- Study on the motion of Side-by-Side moored two ships in consideration of the sloshing influence in tanks (FY2013-2015) 【JSPS Grant-in-Aid JP25289327】
- Study on estimation method of hydrodynamic forces and dynamic tension of underwater linear structures (FY2019-2021) 【JSPS Grant-in-Aid JP19K15232】
- Optical design of position keeping for multi-purpose offshore supply vessel during multi-lift operation (FY2020-2022) 【JSPS Grant-in-Aid JP20H02378】
- Development of a Coupled Motion Estimation Method for Two Ships Considering Mutual Hydrodynamic Interference (FY2023-2026) 【JSPS Grant-in-Aid JP23K26324】
- Modeling and Control for Suspended Flexible Load on Position Keeping Floater (FY2024-2026) 【JSPS Grant-in-Aid JP24K01102】